LONDON: The International Criminal Court’s chief prosecutor Karim Khan has appealed for evidence of atrocities in Sudan, saying his ongoing investigation “seems to disclose an organized, systematic and a profound attack on human dignity.”
However, legal experts who spoke to Arab News have accused the ICC of dragging its feet on the deteriorating situation in Sudan and of focusing too narrowly on the Darfur region while neglecting the wider conflict.
Khan last week said he had become “particularly concerned by the ethnically motivated nature” of the conflict in Sudan after combatants reportedly attacked the main hospital in Al-Fasher, North Darfur, in what likely constituted a war crime.
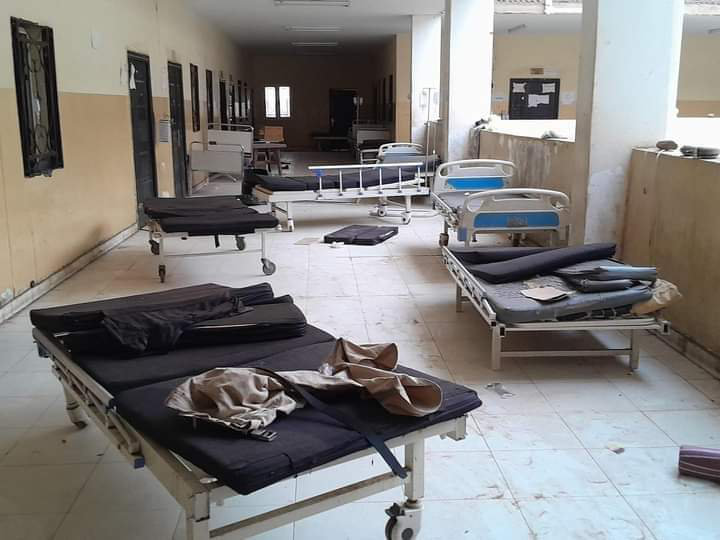
El-Fasher South Hospital in Al-Fasher, North Darfur, after it was attacked. (X: Twitter)
Doctors from the medical charity Medecins Sans Frontieres confirmed to Arab News that the attack on the South Hospital on June 8 had forced MSF and its partners in the Sudanese Ministry of Health to suspend all activities and withdraw staff from the facility.
A spokesperson said authorities had already reduced services at the hospital, with many patients having been transferred before the attack owing to the uptick in fighting around the city — the last in Darfur still under the control of the Sudanese Armed Forces (SAF).
Fighters affiliated with the Rapid Support Forces (RSF), a breakaway military faction that has seized control of swathes of the country since the conflict began on April 15, 2023, were accused of mounting the attack.
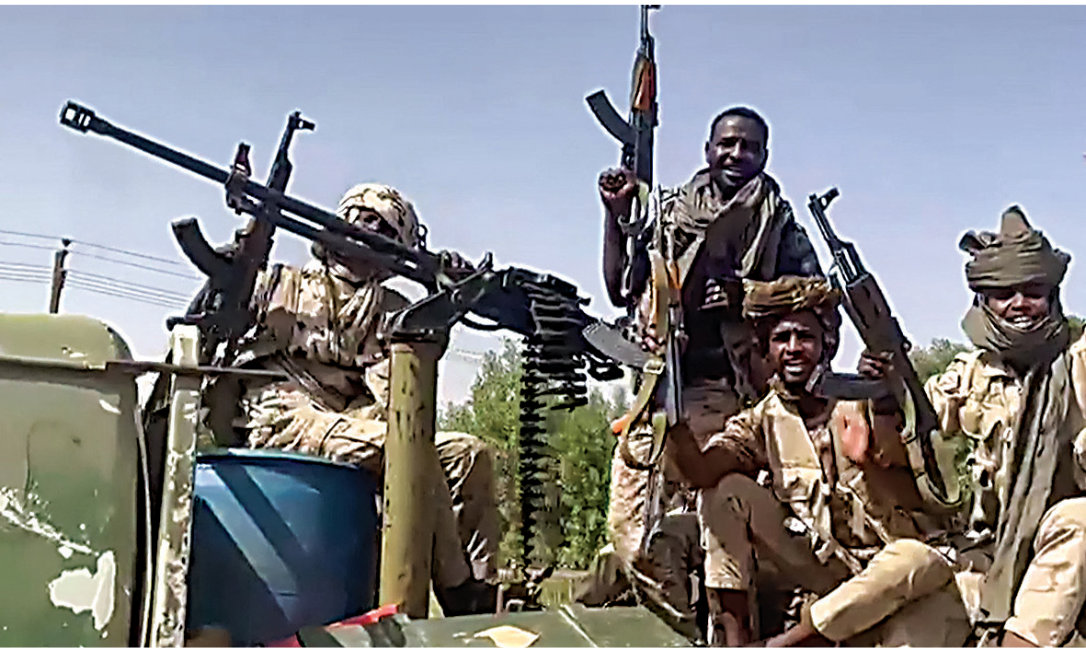

Members of Sudan's paramilitary group known as RSS were accused of burning villages in some parts of the country. (AFP/File)
“It’s outrageous that the RSF opened fire inside the hospital,” Michel Lacharite, head of emergencies at MSF, told Arab News. “It is not an isolated incident. Staff and patients have endured attacks on the facility for weeks from all sides, but opening fire inside a hospital crosses a line.
“Warring parties must stop attacking hospitals. One by one, hospitals are damaged and closed. Remaining facilities in Al-Fasher aren’t prepared for mass casualties, we are trying to find solutions, but the responsibility lies with warring parties to spare medical facilities.”
INNUMBERS
• 14,000 Estimated number of people killed in Sudan since the conflict began on April 15, 2023.
• 10 million People displaced, including over 2 million who have crossed into neighboring countries.
The RSF, commanded by Mohammed Hamdan Dagalo, also known as Hemedti, has previously denied claims that its forces attack civilian infrastructure.
While details about the hospital attack remain sketchy, the MSF spokesperson said “most patients” and “all MSF staff” were able to escape.
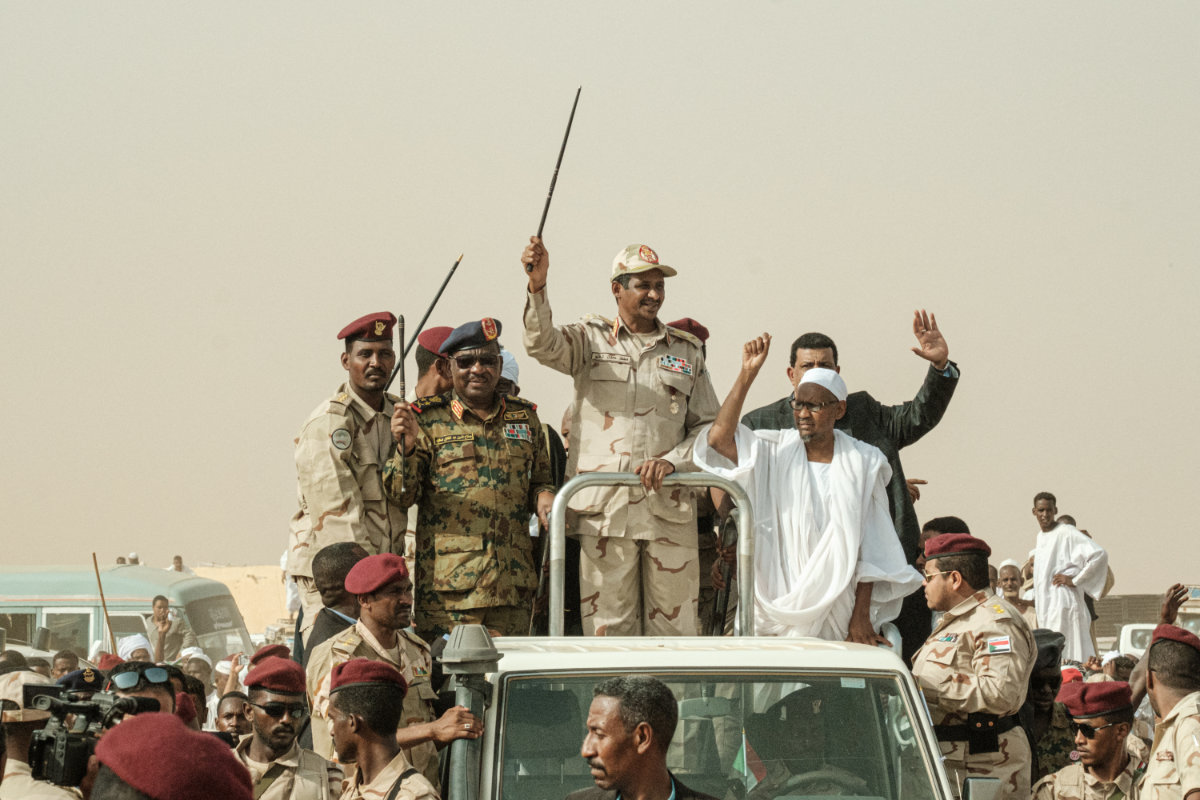

Mohamed Hamdan Dagalo (C), known as Hemeti, commander of the Rapid Support Forces paramilitary, has denied accusations that his group were committing war crimes. (AFP/File)
As the main referral hospital for treating Al-Fasher’s war-wounded, the only one equipped to manage mass casualty events and one of just two with surgical capacity, the loss of services will have a major impact. In less than a month, the facility had treated some 1,300 people.
The UN Security Council adopted a UK-drafted resolution on June 14 demanding an end to the siege of Al-Fasher.
The measure expressed “grave concern” over the spreading violence and reports that the RSF was carrying out “ethnically motivated violence.”
During the meeting, Mohamed Abushahab, the UAE’s ambassador to the UN, said: “We believe that the Sudanese people deserve justice and peace. They need a ceasefire, a credible political process and unhindered flow of humanitarian aid.”
Rebutting accusations made by the representative of Sudan’s SAF-backed government, he said: “Excuses and finger pointing only prolongs the suffering of civilians.”
Independent ivestigations using videos suggest recent SAF victories were enabled by the deployment of such Iranian-made combat drones as Mohajer-6 and Zajil-3.
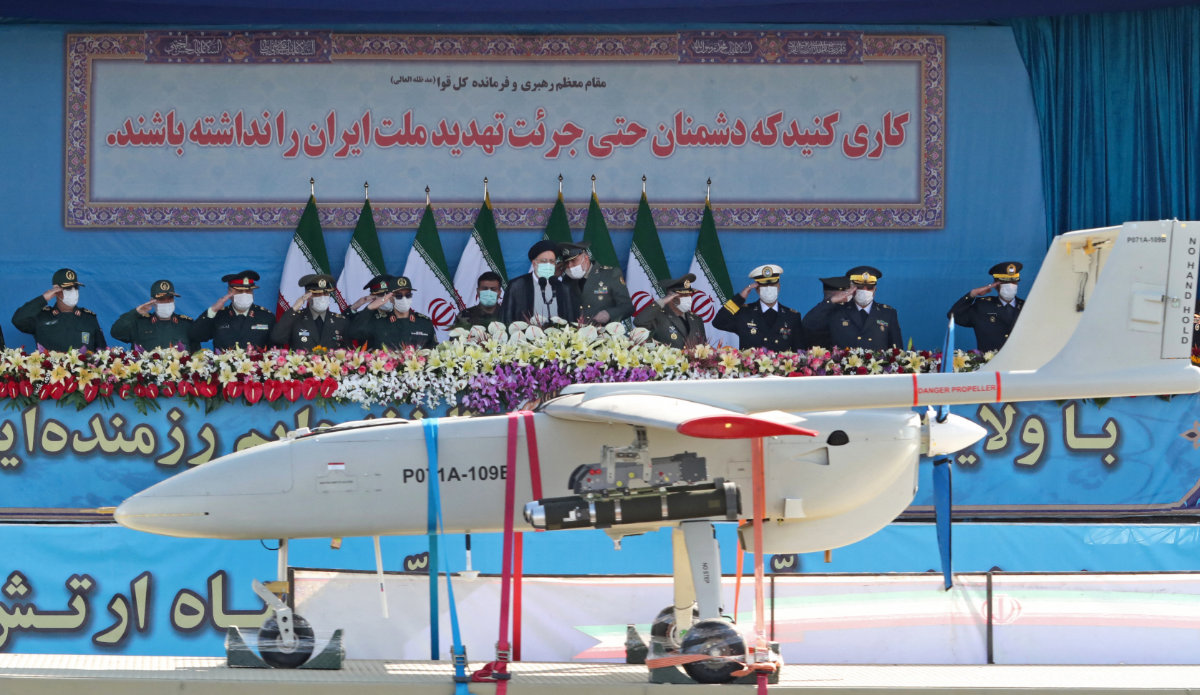

A handout picture provided by the Iranian presidency on April 18, 2022 shows an Iranian combat drone on display during a military parade in Tehran. Independent investigations using videos suggest recent SAF victories were enabled by the deployment of such Iranian-made combat drones. (AFP/File)
According to Wim Zwijnenburg, a drone expert and head of the Humanitarian Disarmament Project at Dutch peace organisation PAX, the videos are “an indication of active Iranian support” for SAF.
“If these drones are equipped with guided munitions, it means they were supplied by Iran because those munitions are not produced in Sudan,” Zwijnenburg told BBC.
Sudan’s SAF-dominated governing council has denied acquiring weapons from Iran.
Cameron Hudson, a senior fellow for the Africa Program at the Center for Strategic and International Studies, said that although the Al-Fasher hospital assault has been a wake-up call for the ICC, attacks of this kind were “nothing new.”
“The fact of the matter is that this is not the first hospital to be looted or destroyed in this conflict,” Hudson told Arab News.
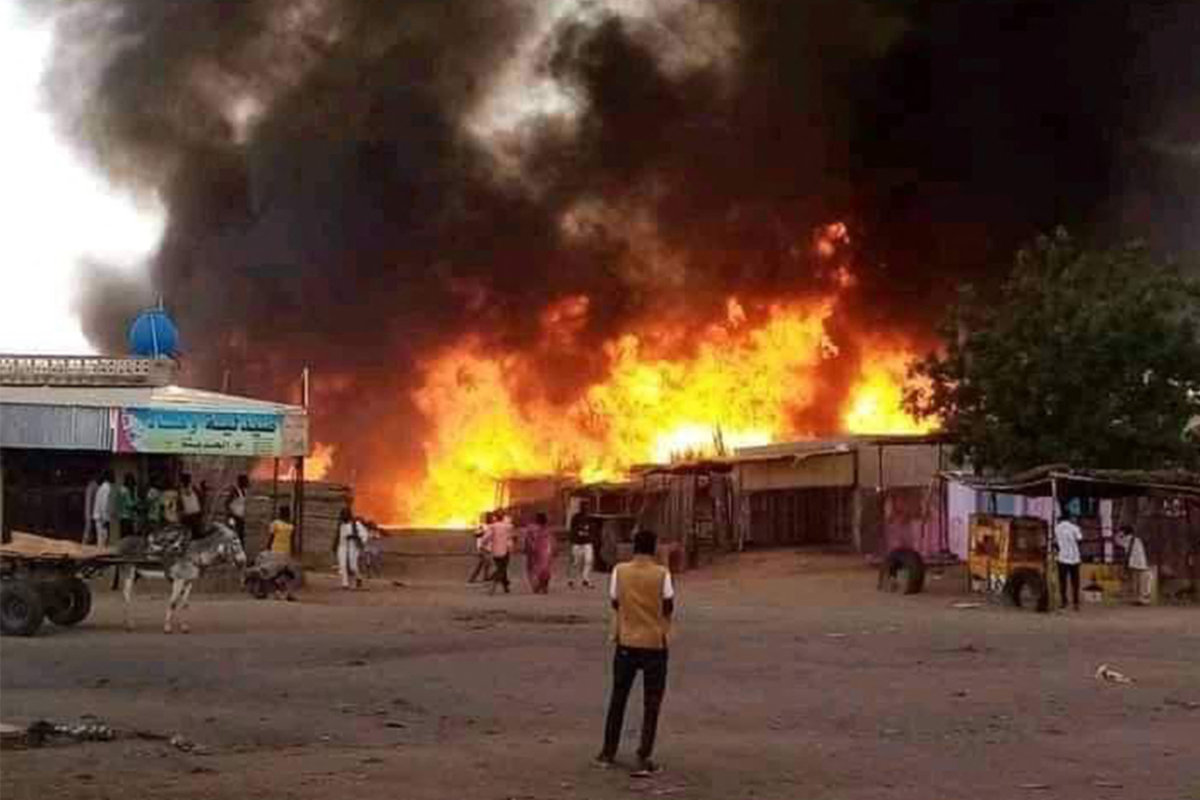

Fire rages in a livestock market area in al-Fasher, the capital of Sudan's North Darfur state, on September 1, 2023, in the aftermath of bombardment by the paramilitary Rapid Support Forces (RSF). (AFP/File)
“It is a conflict that has been raging for 14 months and has been fought in much the same way with this attack well within the nature of the conflict.
“What is new is that Sudan’s civilian population’s ability to withstand the shocks of this war has depleted. But while it may feel like a game-changing moment, it is not.”
Referring to the July 1995 massacre of more than 8,000 Bosniak Muslim men and boys during the Bosnian War, Hudson said: “Maybe if there was a Srebrenica moment, a move to extermination, that would be game-changing.”
Khan’s comments indicate the ICC has been paying attention to the situation in Sudan. However, Hudson voiced disappointment at the court’s slow response to the conflict.
Contrasting the “alacrity” with which the ICC acted against Russia for its war in Ukraine and Israel for its assault on Gaza, he said it was telling of Sudan’s ranking in international priorities that the court was “only now” investigating.
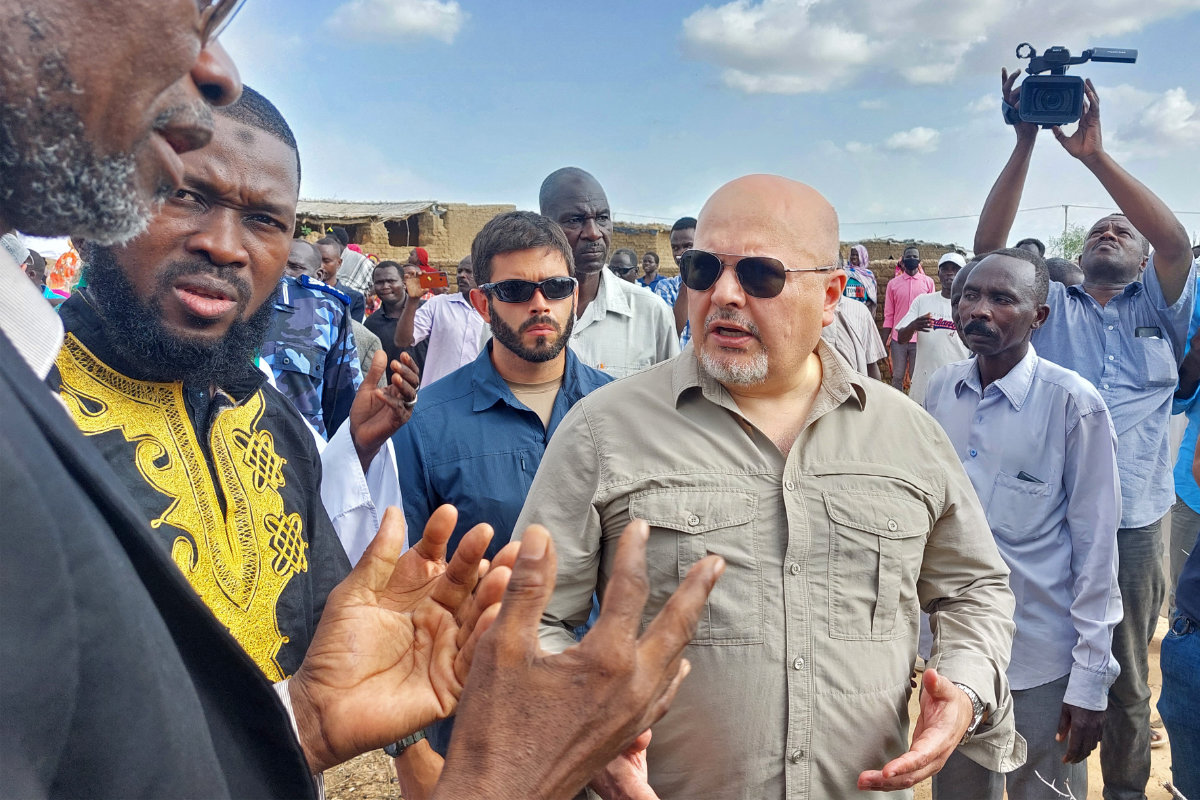

International Criminal Court's chief prosecutor Karim Khan (L) visits the Kalma camp for internally displaced people in Nyala, the capital of South Darfur, on August 21, 2022. (AFP/File)
“Khan’s comments strike me as an admission that the court has not moved at pace and should have been doing more,” said Hudson. “I am not sure what restraints he is operating under but he’s not prioritized Sudan, and, in Darfur, these cases build themselves.
“It is not just the court, this conflict has been neglected more broadly, there need to be moves to build a diplomatic process and to get humanitarian aid because only eight percent of a global appeal has been met, which is shockingly low.
“I would like to see an increase in the cost on this war’s actors as part of a move to bring it to an end, including the use of sanctions, which have not been deployed efficiently, and could have a part to play in bringing actors to the negotiating table.”
Although efforts at brokering a ceasefire between the two sides have so far failed, Saudi aid agency KSrelief has been rolling out health projects intended to support Sudan’s civilian population, with three projects put into action in the last week alone.
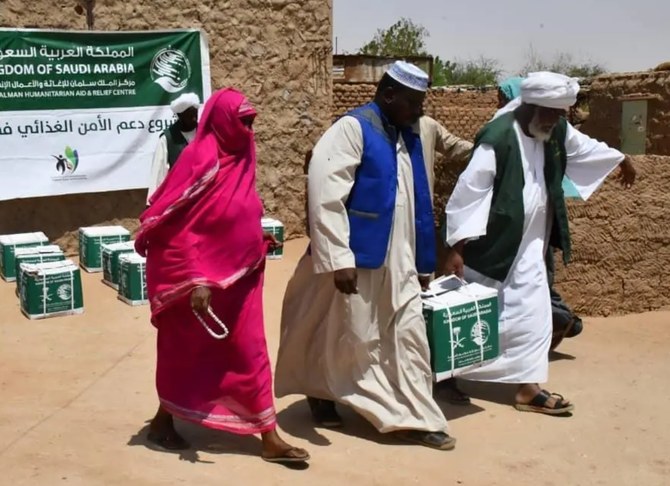

Sudanese villagers receive humanitarian aid from Saudi Arabia at a KSrelief center in Khartoum, Sudan. (SPA/File)
With thousands of civilians reportedly killed and thousands more displaced by the fighting across Darfur, the ICC’s machinery has swung into action. Even so, Sudanese international lawyers have expressed skepticism.
One who spoke to Arab News on the condition of anonymity said they were particularly concerned by Khan’s focus on the violence in Darfur when in reality, the violence has spread far beyond the troubled western region.
“The ICC was mandated to investigate crimes in Darfur in 2005, and we have not yet seen any results from that mandate, and now this conflict is happening in other areas,” the lawyer said. “This violence is not all in — nor is it originating from — Darfur.
“What is happening outside Darfur is not lesser than the violence happening within it and yet the ICC, partly as a consequence of Sudan not being a party to the court’s jurisdiction, is drawing attention away from this and making it all about Darfur.”
Despite lacking jurisdiction as a consequence of the Sudanese government failing to ratify the ICC treaty, otherwise known as the Rome Statute, the court had gained jurisdiction for a limited investigation into earlier crimes in Darfur through a UN Security Council referral.
That referral resulted in the ICC’s 2009 decision to issue an arrest warrant for the since-ousted Sudanese President Omar Bashir for multiple charges, including for a genocide that took place in Darfur between 2003 and 2008.

Sudan's former strongman Omar Bashir (left) was the subject of an arrest warrant issued by the ICC over genocide charges committed in Darfur between 2003 and 2008 allegedly by the RSF led by General Mohammed Hamdan Dagalo (right)
Born out of Arab militias commonly known as Janjaweed, the RSF was mobilized by Bashir against non-Arab tribes in Darfur. At the time, they were accused of mass killings, rapes and other atrocities, and Darfur became synonymous with genocide.
Welcoming Khan’s push for evidence, another Sudan-based legal expert, who spoke to Arab News anonymously, challenged those questioning the focus on Darfur, stressing it made sense given the region’s history.
“Does it make sense to keep looking at cases within the Darfur geographic region? Yes, because all that is happening in Sudan from 2003 up to now can be connected back to Darfur, as that is where this conflict’s root causes lie,” they said.
“There are questions to be asked though in relation to how the ICC is addressing the Darfur case and the role that this, and the coverage of it, will have around the protection of civilians as what is needed is to reduce that risk.”
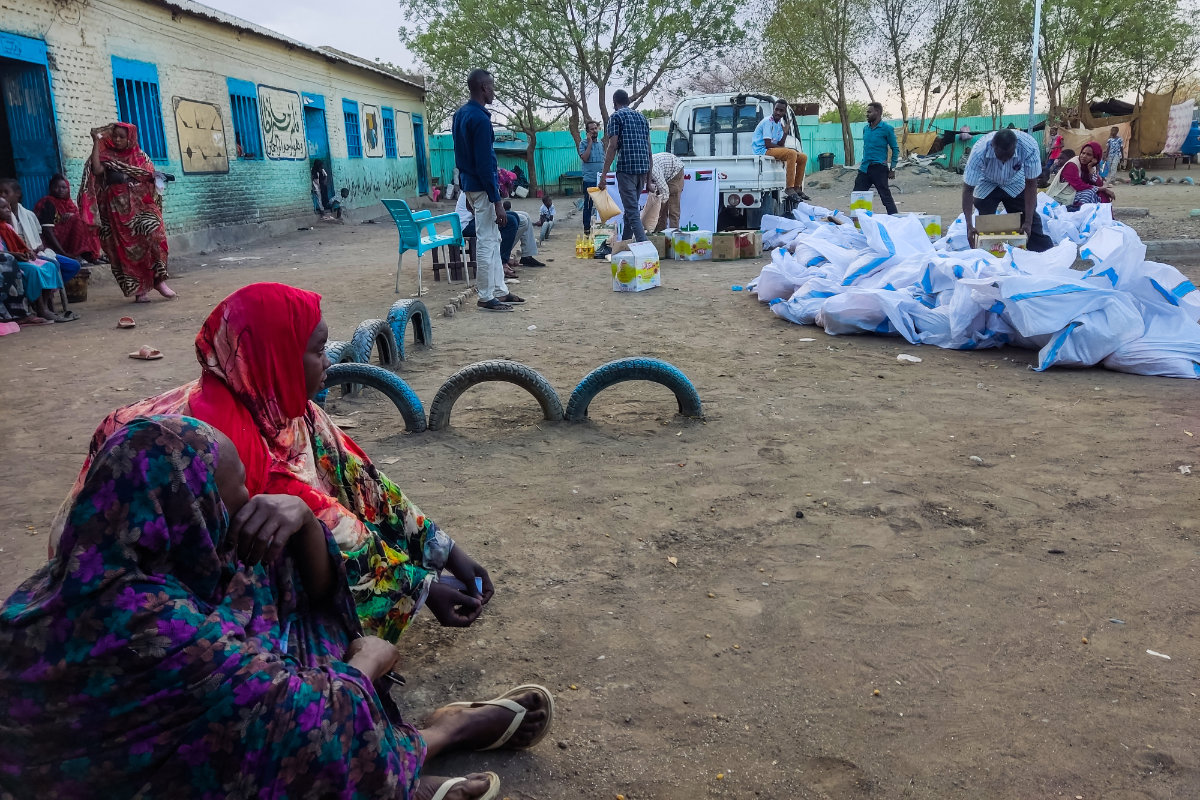

Internally displaced women wait to collect aid from a group at a camp in Gadaref on May 12, 2024. (AFP/File)
The war in Sudan has cost the lives of more than 14,000 people and left thousands more wounded while pushing the population to the brink of famine.
The UN warned the warring parties last month that there is a serious risk of widespread starvation in Darfur and elsewhere in Sudan if they do not allow humanitarian aid into the region.
The war has also created the world’s largest displacement crisis as more than 10 million people have been forced to flee their homes, including over 2 million people who have crossed into neighboring countries.
Saudi Arabia has played a central role in facilitating talks between the two warring factions, urging them to meet their obligations to protect civilians under both the Jeddah Declaration and the requirements of international humanitarian law.





























